List of state and union territory capitals in India
| States and territories of India by: |
|---|
| Area |
| Population |
| Highest Point |
| GDP |
| HDI |
| Tax revenues |
| Voters |
| Abbreviations |
| Natural growth rate |
| Vaccination |
| Literacy rate |
| Electricity |
| Capitals |
| Media exposure |
| Origin of name |
| HIV awareness |
| Household size |
| Underweight people |
| Place of worship |
| TV ownership |
| Transport network |
| Power capacity |
India is divided into twenty-eight states and seven union territories (UTs). States have their own government, whereas union territories are administered by the Central government. As per the Constitution of India, the central government can also empower a union territory with a legislature. As of 2008[update], two union territories, the National Capital Territory of Delhi and Puducherry have their own legislatures.
The state and union territory capitals are sorted according to the administrative, legislative and judicial capitals. The administrative capital is where executive government offices are located, the legislative capital is where the state assembly convenes, and the judicial capital is the location of the territorial High Courts of India.
States and territories
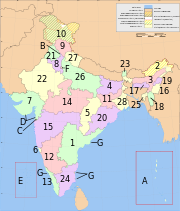
States:
Union Territories:
Notes
- ↑ Andhra Pradesh was formed combining erstwhile Andhra state and Telugu speaking region of Hyderabad state (Telangana). Capital of Andhra state was Kurnool.
- ↑ Shillong was the joint capital of Meghalaya and Assam in 1971, after Meghalaya split from Assam.
- ↑ Chandigarh is the capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana, and is a Union Territory, separate from the two states.
- ↑ Panaji was the capital of Goa from 1843 when it was ruled by the Portuguese.
- ↑ Nagpur was the capital of Central Provinces and Berar which was a province from 1861 until 1950. It became the major constituent of Madhya Pradesh, after it was formed in 1950. Nagpur remained the capital of the new state. In 1956, Berar (Vidarbha) was separated from Madhya Pradesh, and merged with the Bombay State. Nagpur thus lost the status of a capital city. In 1960, under the Nagpur pact, Nagpur became the second capital of Maharashtra.
- ↑ Mumbai (Bombay) was the capital of Bombay Presidency which was a province until 1950. After that it became the capital of Bombay State, which was split into Gujarat and Maharashtra in 1960.
- ↑ In 1960, under the Nagpur pact, Nagpur became the second capital of Maharashtra. Although an official notification to this effect was only given in 1988. The India yearbook of the government of India still does not mention Nagpur, being either the second or winter capital of Maharashtra.
- ↑ Under the Nagpur pact, one of the preconditions for Vidarbha joining the state of Maharastra was that, at least one of the legislative sessions every year should be held in Nagpur. This session is supposed to specially deal with Vidarbha's problems.
- ↑ Lahore was the capital of Punjab when the state was created in 1936. It is now a part of Pakistan.
- ↑ Gangtok has been the capital of Sikkim since 1890. Sikkim joined the Indian Union in 1975.
- ↑ Chennai (Madras) was the capital of the Madras Presidency since 1839, which was redrawn as Tamil Nadu in 1956.
- ↑ Dehradun is the provisional capital of Uttaranchal. The town of Gairsen is being built as the state's new capital.orissa's previous name was kalinga
References
- THOMAS (2003). Manorama Year Book 2003 pgs 649-714. Malayala Manorama Co. Ltd. ISBN 81-900461-8-7.
- "Jurisdiction and Seats of Indian High Courts". Eastern Book Company. http://www.ebc-india.com/lawyer/hcourts.htm. Retrieved August 3, 2005.
- "A Brief Historical Profile of Assam Legislative Assembly". Assam Legislative Assembly. http://assamassembly.nic.in/history.html. Retrieved August 3, 2005.